Testicular Cancer
Introduction
Cancer which has one of the highest curable rates, testicular cancer is also the rarest form of cancer amongst Indian men. Testicular cancer is not common: about 1 of every 250 males will develop testicular cancer at some point during their lifetime.
Testicular cancer is a form of cancer that occurs in the testes, or testicles. Testicular cancer affects the testicles, which produce male sex hormones and sperm used for reproduction. In most instances, there is no clear-cut cause behind testicular cancer. The problem occurs when healthy cells in the testicle are altered and start growing and dividing rapidly, to the point where no new cells are needed. This causes accumulating cells to form a mass in the testicle.
Testicular cancer, which generally affects men between the ages of 15 and 35, is a form of cancer that originates in one or both testes or testicles.
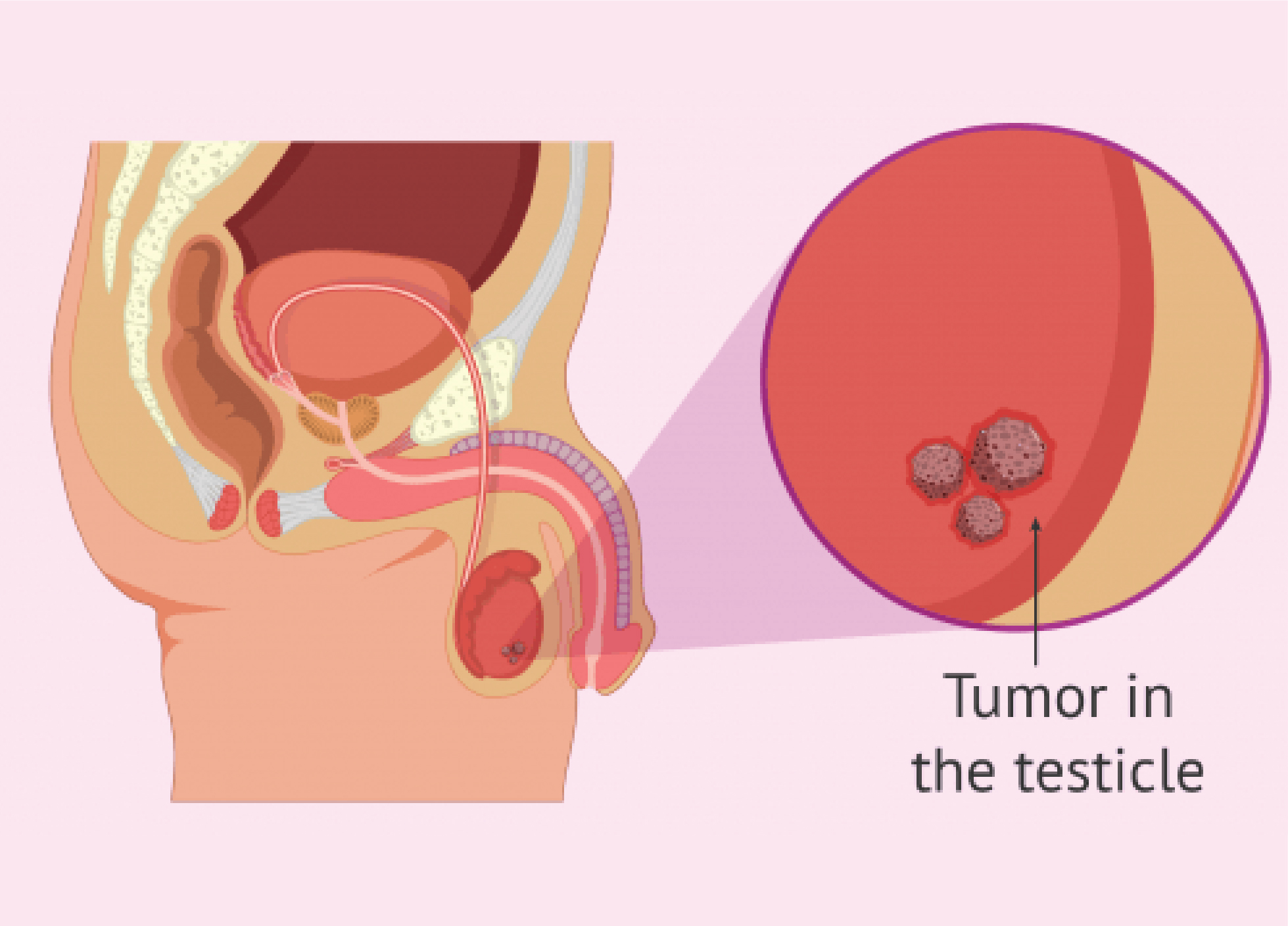
Types of Testicular Cancer:
There are two main types of testicular cancer:
Causes
The exact cause of testicular cancer is poorly understood. However, some factors may increase a man's risk of developing testicular cancer.
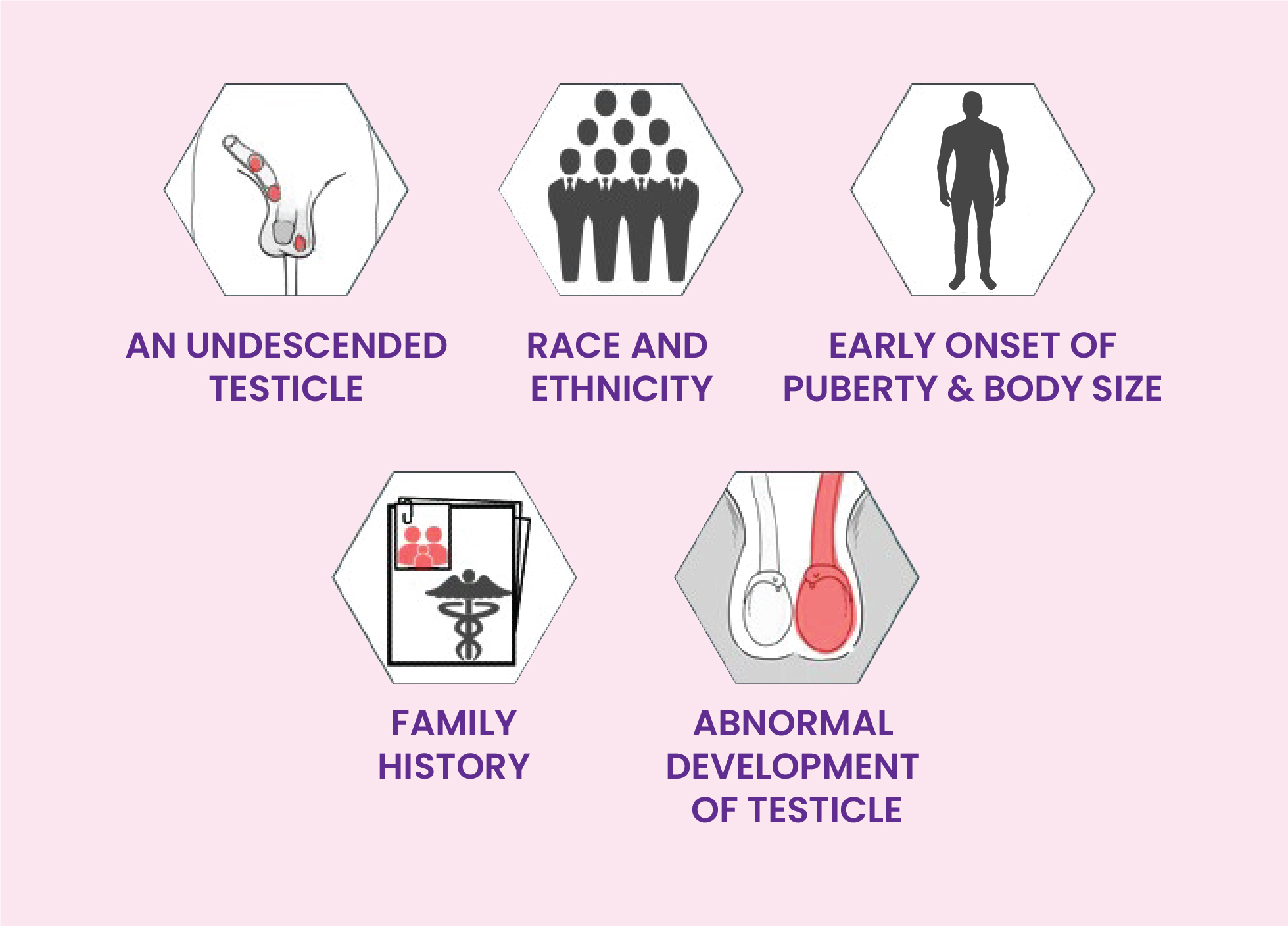
Risk factor
There are many risk factors associated with testicular cancer, and these include:
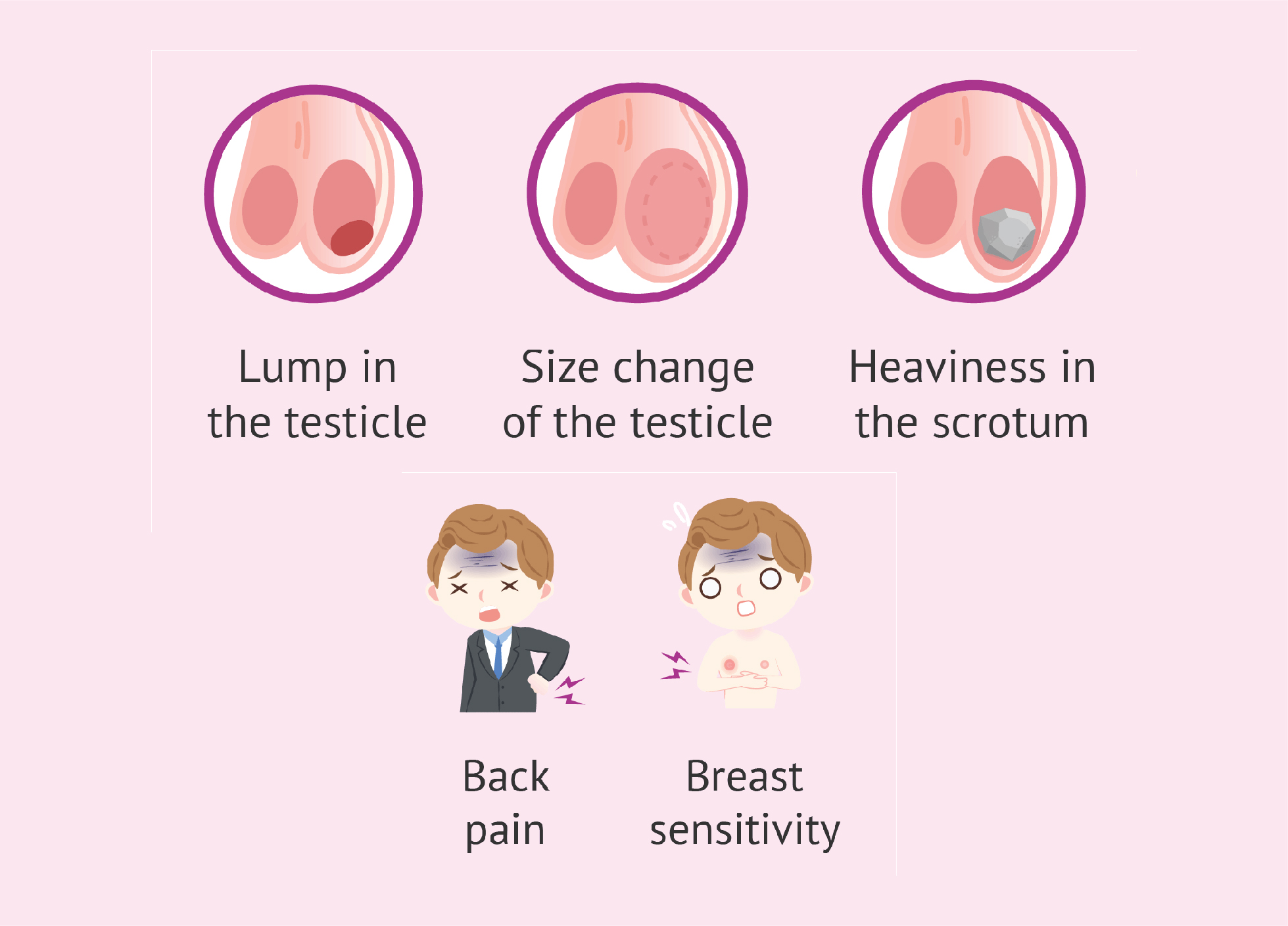
Signs & Symptoms
Some men show no symptoms when diagnosed with testicular cancer. When symptoms appear, they include:
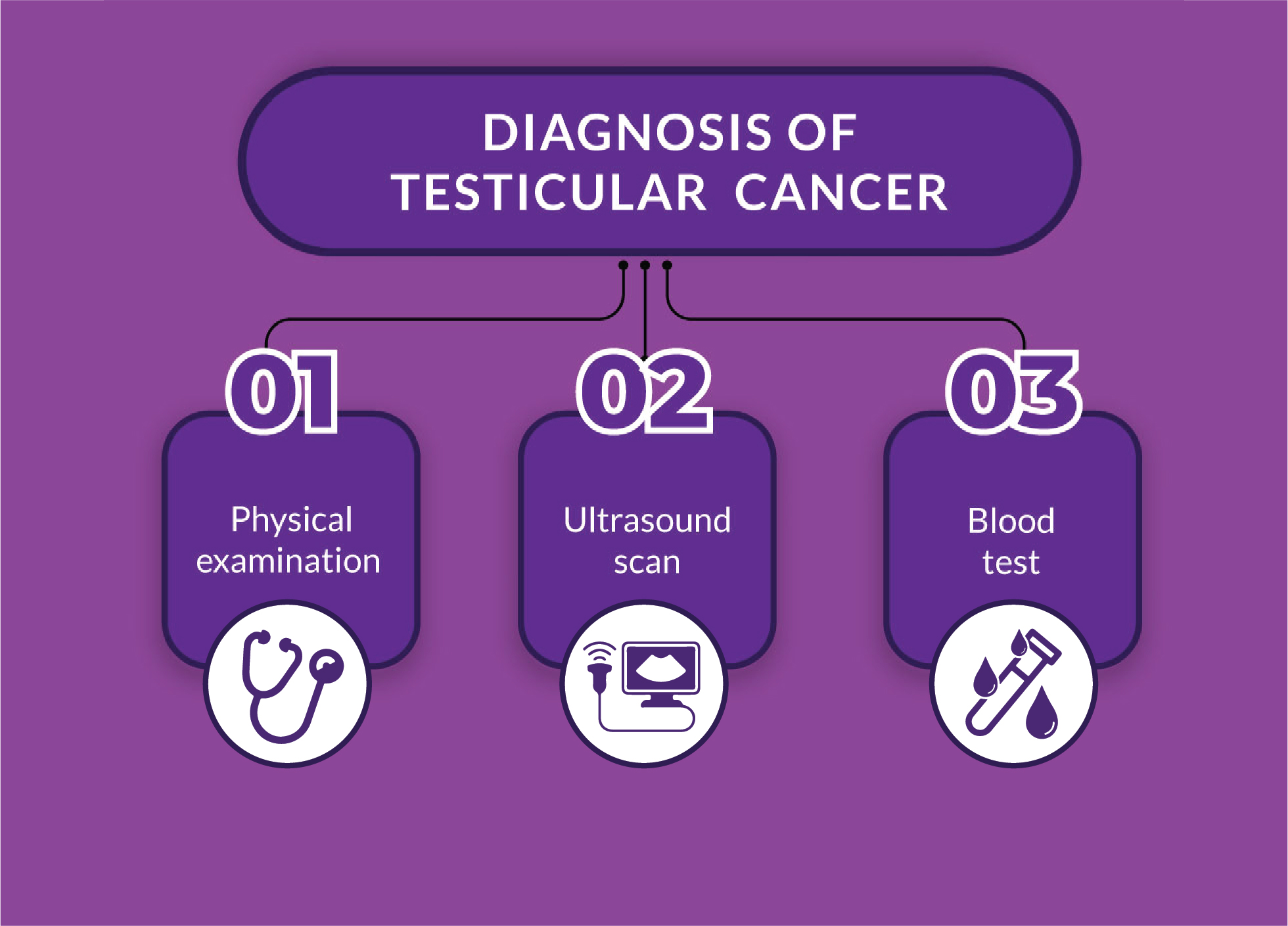
Diagnosis
Treatment for testicular cancer is highly effective whendiagnosed in an early stage. An expert would first conduct a physical examination to check for the signs of testicular cancer. The doctor may also check other parts of the body followed by other diagnostics which include:
The diagnosis includes:
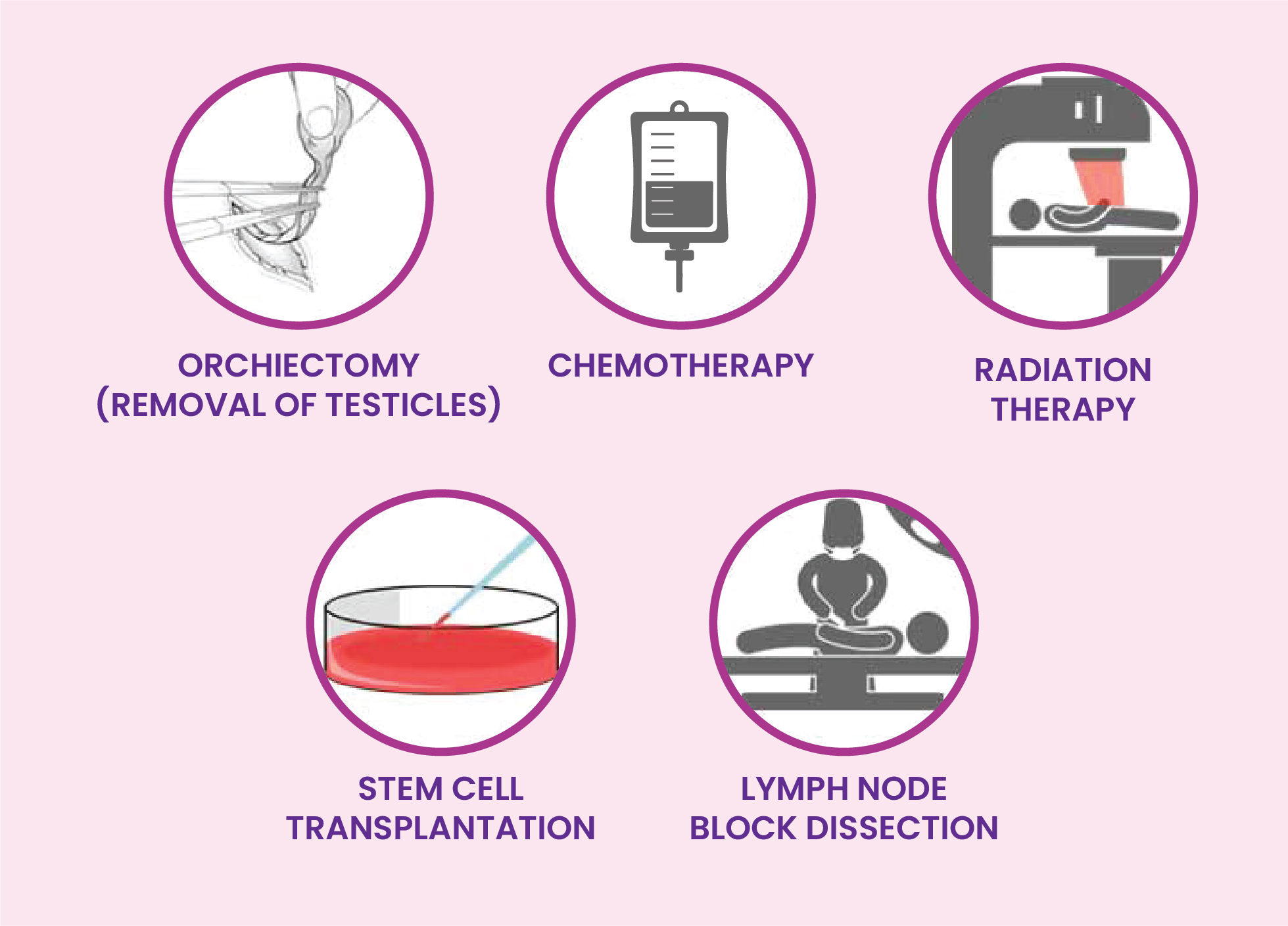
Management
There are three general categories of treatments used for testicular cancer. Depending on the stage of cancer, you may be treated with one or more options.
Follow-Up
Follow-up visits for testicular cancer are usually scheduled for 5 to 10 years after the initial treatment: every 2 to 6 months for the first 3 years. Every 6 to 12 months after 3 years.
