Bone Cancer Specialist in Delhi
Who is the top bone cancer specialist in Delhi?
If you are looking for a bone cancer specialist in Delhi, you should consider doctor Dr Priya Tiwari. She is an expert in treating various cancers, including bone cancer. With her tailored treatment, you will be able to fight against cancer.
What is meant by Ortho-Oncology?
Ortho-Oncology, commonly referred to as orthopaedic oncology, is a medicine that focuses on tumours and cancers of the arteries, muscles, nerves, cartilage, fibrous tissues, and bones. Oncologists who specialize in treating tumours and other diseases of the bone, joints, and muscles are known as orthopaedic surgeons.
Are there any signs of bone cancer? Is it treatable?
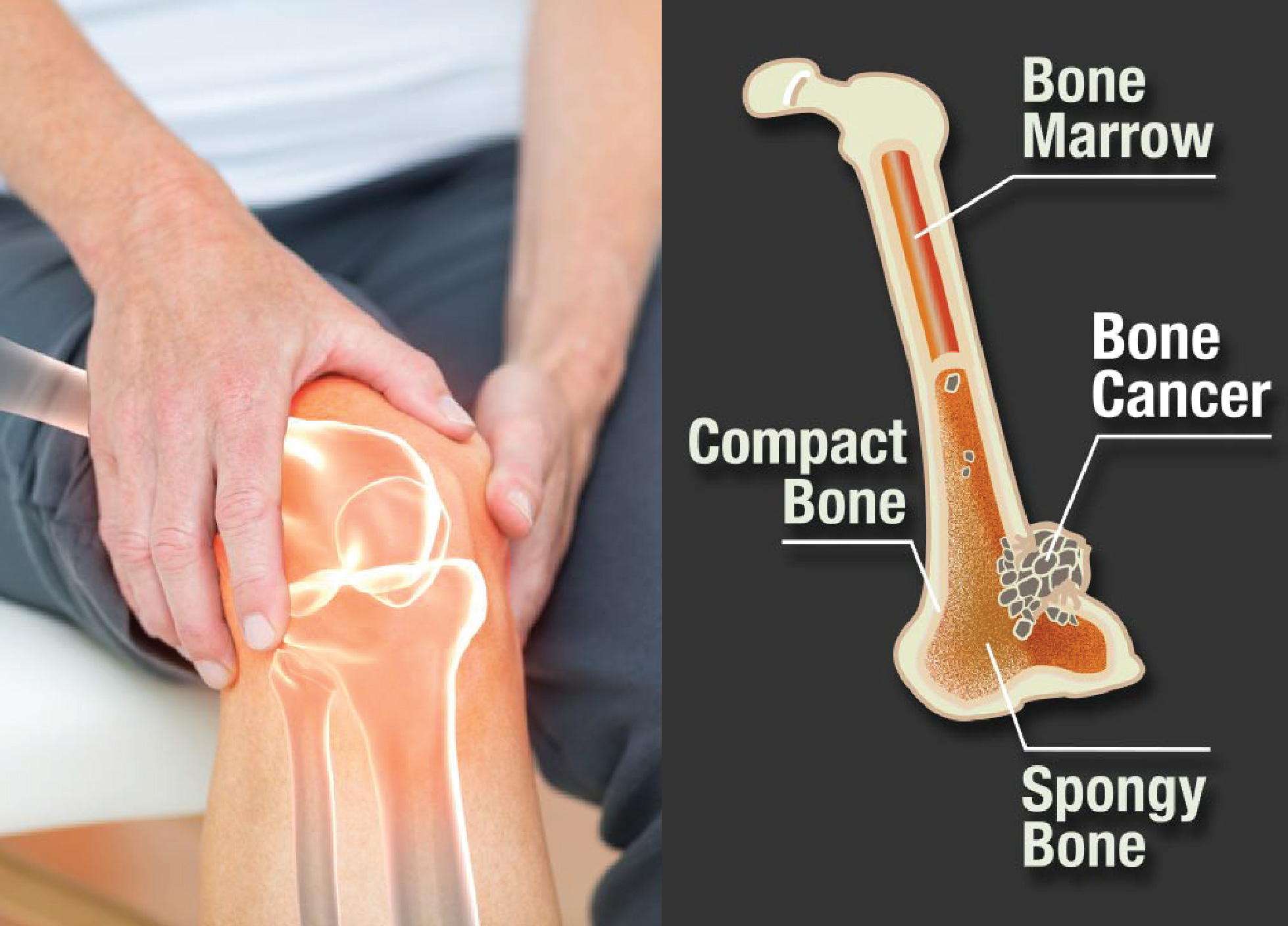
The phrase "bone cancer" refers to various malignancies that manifest in the bones. Cancerous cells can damage healthy bone tissue if they spread throughout a bone. The type of bone cancer depends on the cell and tissue types where the disease first manifests itself.
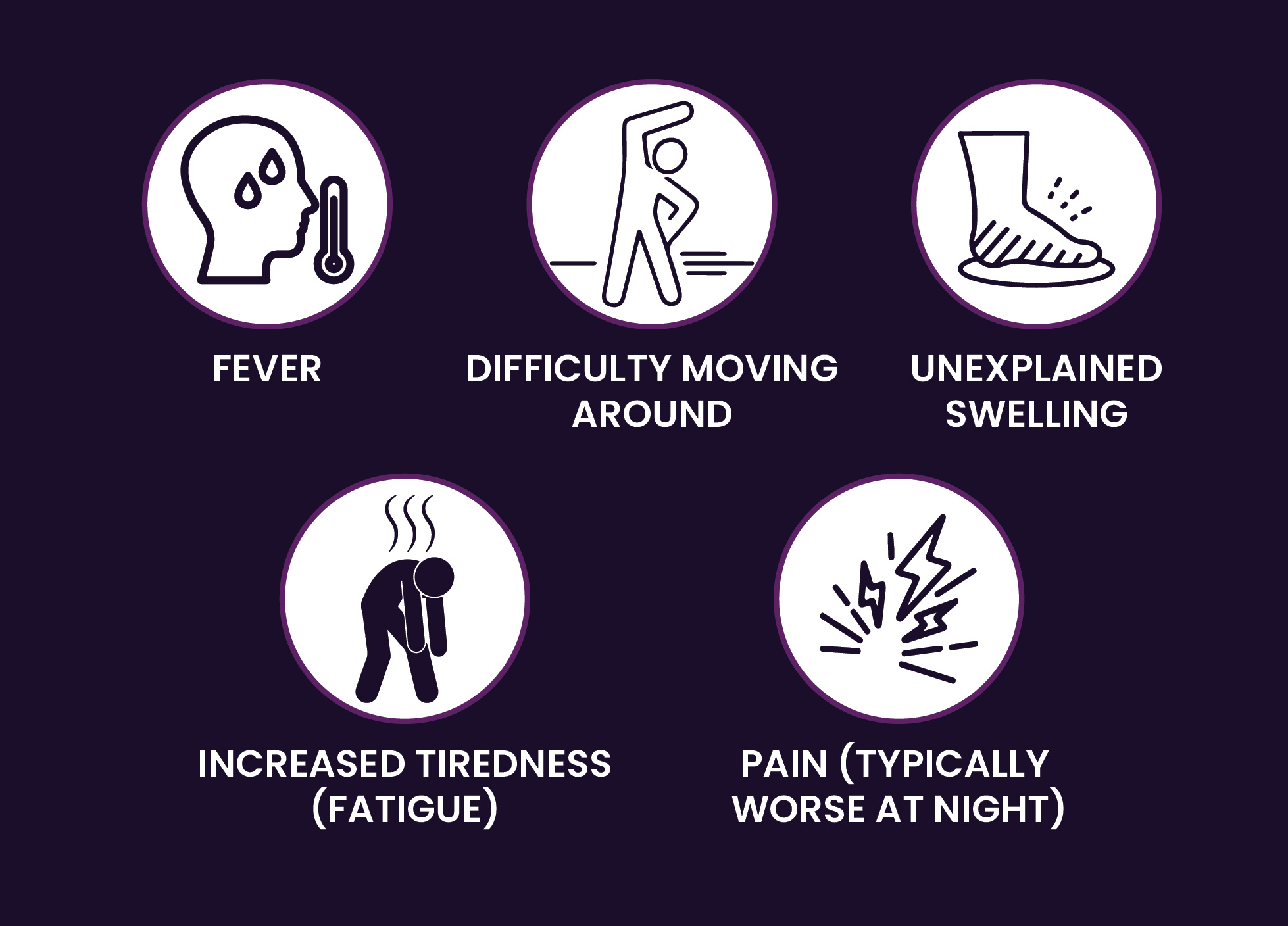
A lump that causes no pain may be the only symptom bone cancer patients may experience. Others may have a range of symptoms. Certain disorders like arthritis or Lyme disease may also induce these symptoms, which could cause a delay in diagnosis. Some of the more typical indications of bone cancer are:
The type of bone cancer an individual has, its spread, and that individual's general health; all determine how it is treated. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy are the primary forms of treatment.
What does a bone cancer specialist do to diagnose bone cancer?
Bone-care specialists frequently utilize X-rays to view images of your bones before making a diagnosis of bone cancer. Before receiving any treatment, MRI and CT scans are frequently performed to produce more precise images of the regions around the bones.
Bone care specialists will perform a biopsy, in which a small sample of bone tissue is extracted and studied under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis. A biopsy reveals particular details about the tumour, including how it developed. Knowing this information helps doctors determine the optimal treatment strategy for a particular tumour.
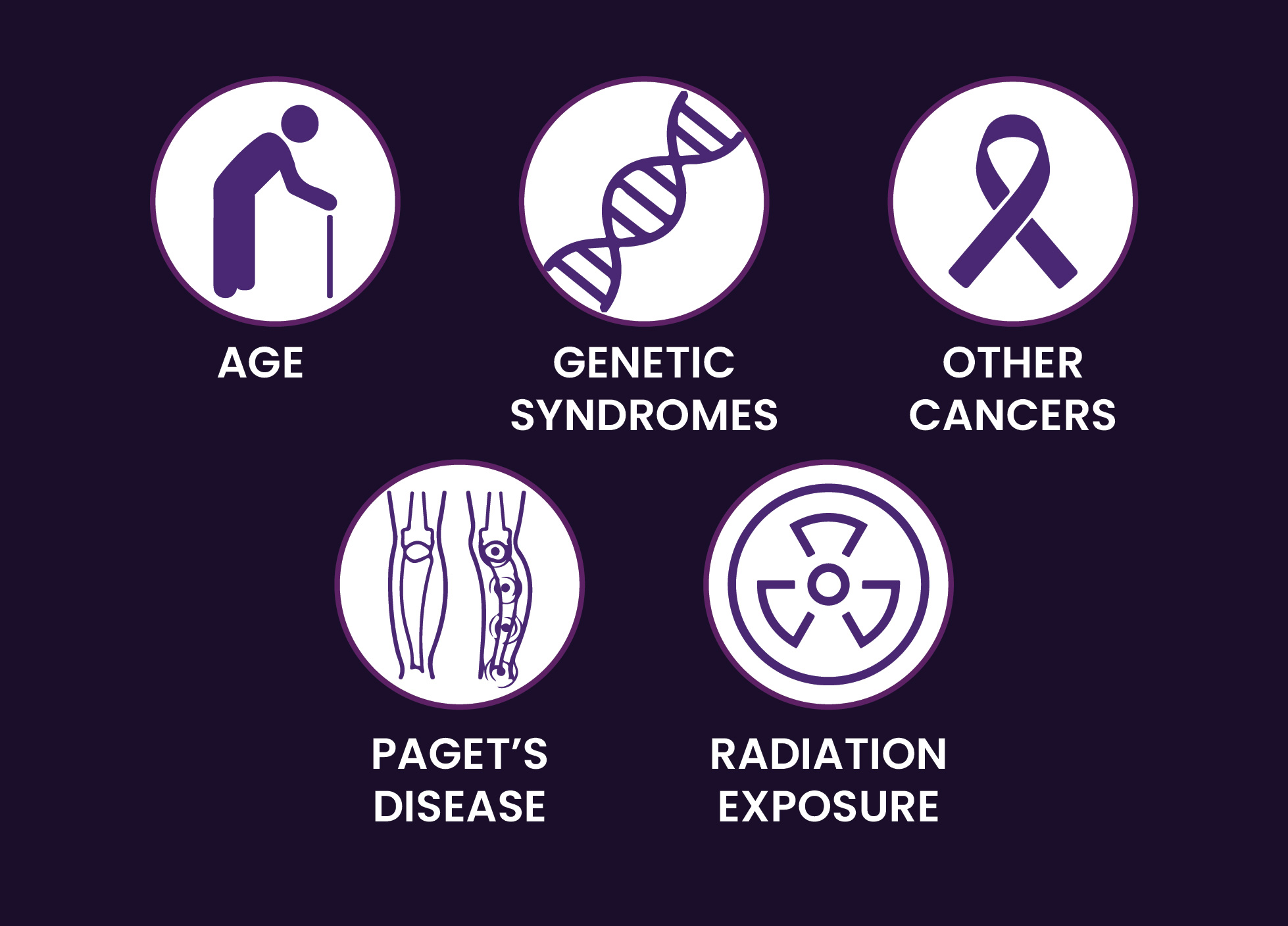
What are the risk factors for bone cancer?
There are several risk factors associated with bone cancer, including:
Heredity - A minor percentage of cases of bone cancer is genetic. Children with genetic retinoblastoma, a rare form of eye cancer, are more likely to acquire osteosarcoma. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome, multiple exostoses syndrome, and tuberous sclerosis are other inherited diseases connected to certain forms of bone cancer.
Age - Teenagers and children whose bones are still growing or have only just finished growing are more likely to develop bone cancer.
Previous cancer treatment - People undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy for other diseases, including other cancers, are more likely to develop bone cancer.
Paget's Disease - Osteosarcoma risk may be higher in adults with Paget's disease. The irregular formation of new bone cells characterizes this benign disease. Paget's disease-affected bones are heavier and thicker than typical bones but weaker and more prone to breaking.