Liver Cancer
Introduction
Liver cancer is emerging as one of the fastest-spreading cancers in India. India sees about 3-5 cases of liver Cancer per 1, 00,000 people which translates to 30,000-50,000 new cases per year. Liver cancer is a disease in which harmful cancer cells develop in the tissues of the liver. Primary liver cancer occurs when the cancer cells start in the liver, and the different types of primary liver cancers are usually named after the types of cells from which cancer has developed.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or hepatoma comes from the main cells of the liver called hepatocytes and makes up about 85% of primary liver cancers. A less common type of primary liver cancer starts from cells that line the bile duct called cholangiocytes and is therefore called cholangiocarcinoma or bile duct cancer.
The liver is also the site of another type of cancer called secondary, or metastatic, liver cancer. In this condition, main cancer begins elsewhere in the body and secondary deposits are formed in the liver. A common example is a colorectal cancer spreading to the liver through the bloodstream.
Causes:
In most cases, the cause of liver cancer is long-term damage and scarring of the liver (cirrhosis). Cirrhosis may be caused by:
Risk factor
The risk factors of liver cancer include :

Signs & Symptoms
Most of the times liver cancer does not show signs and symptoms in the initial stage and as cancer begins to grow symptoms gradually show up. To detect liver cancer at early stage doctors often recommend screening and examination of the liver (at least once a year) to avoid the risk of cancer. Signs and symptoms of liver cancer include:

Diagnosis
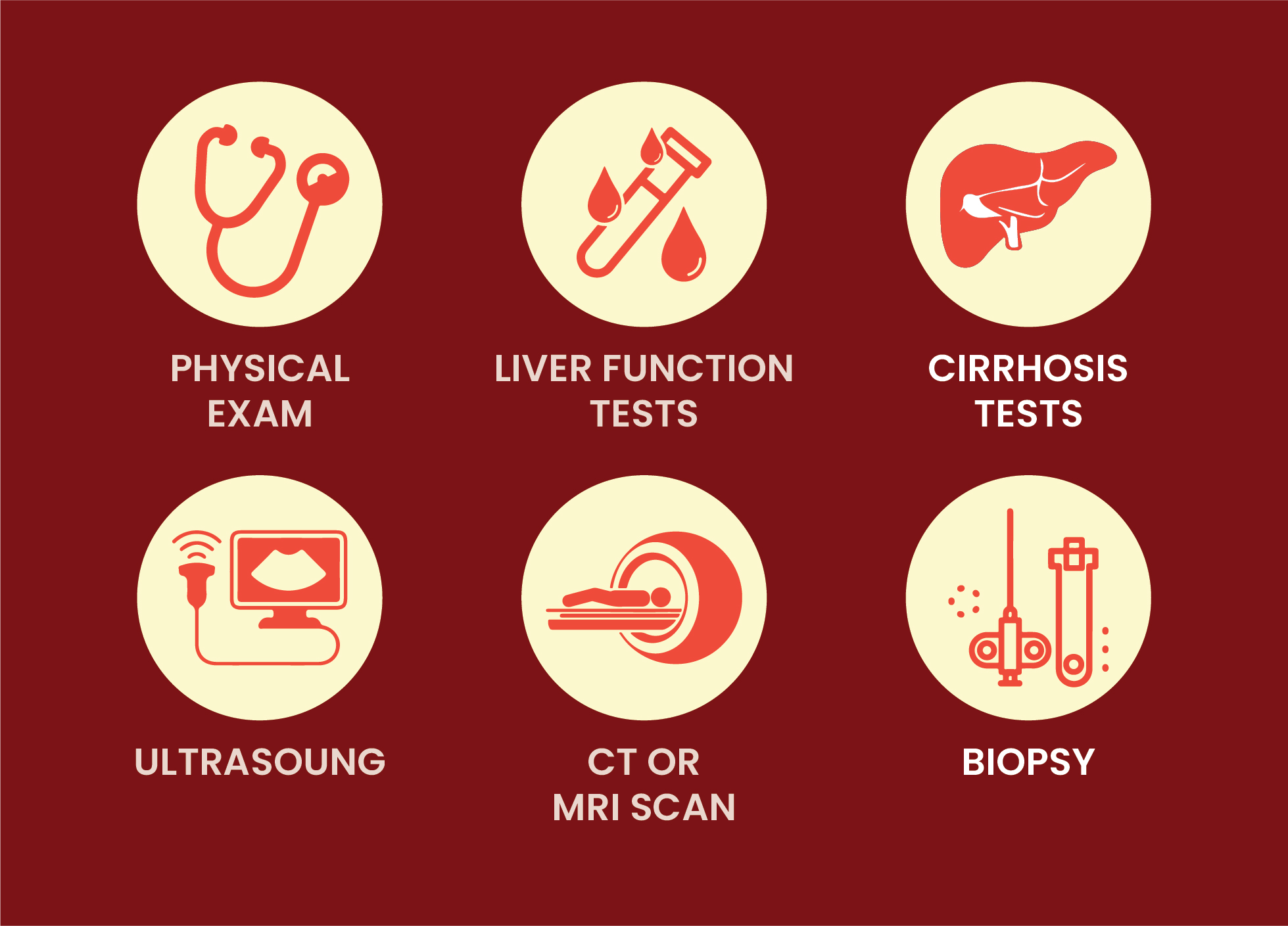
Based on the stage of the liver cancer the diagnosis is carried forward. Before the treatment, the doctor recommends a few tests and procedures that help to diagnose the extentto which liver cancer has developed or spread.
The following tests and procedures include:
Management
The type of treatment for patients with liver cancer will depend on its stage and the patient’s general health. The main treatments used are surgery, tumor ablation (removal), chemotherapy, targeted cancer therapy, and radiotherapy.
Follow-Up
If you have been treated with surgery, a liver transplant, or ablation/embolization and have no signs of cancer remaining, most doctors recommend follow-up with imaging tests and blood tests every 3 to 6 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 to 12 months. Follow-up is needed to check for cancer recurrence or spread, as well as possible side effects of certain treatments.
