Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer is the eighth most common cancer with a yearly prevalence of 456000 new cases. In India, it's the fourth most common cause of cancer- related deaths. Esophageal cancer starts when cells in the lining of the esophagus begin to grow out of control. Men are more likely to get esophageal cancer compare to women.
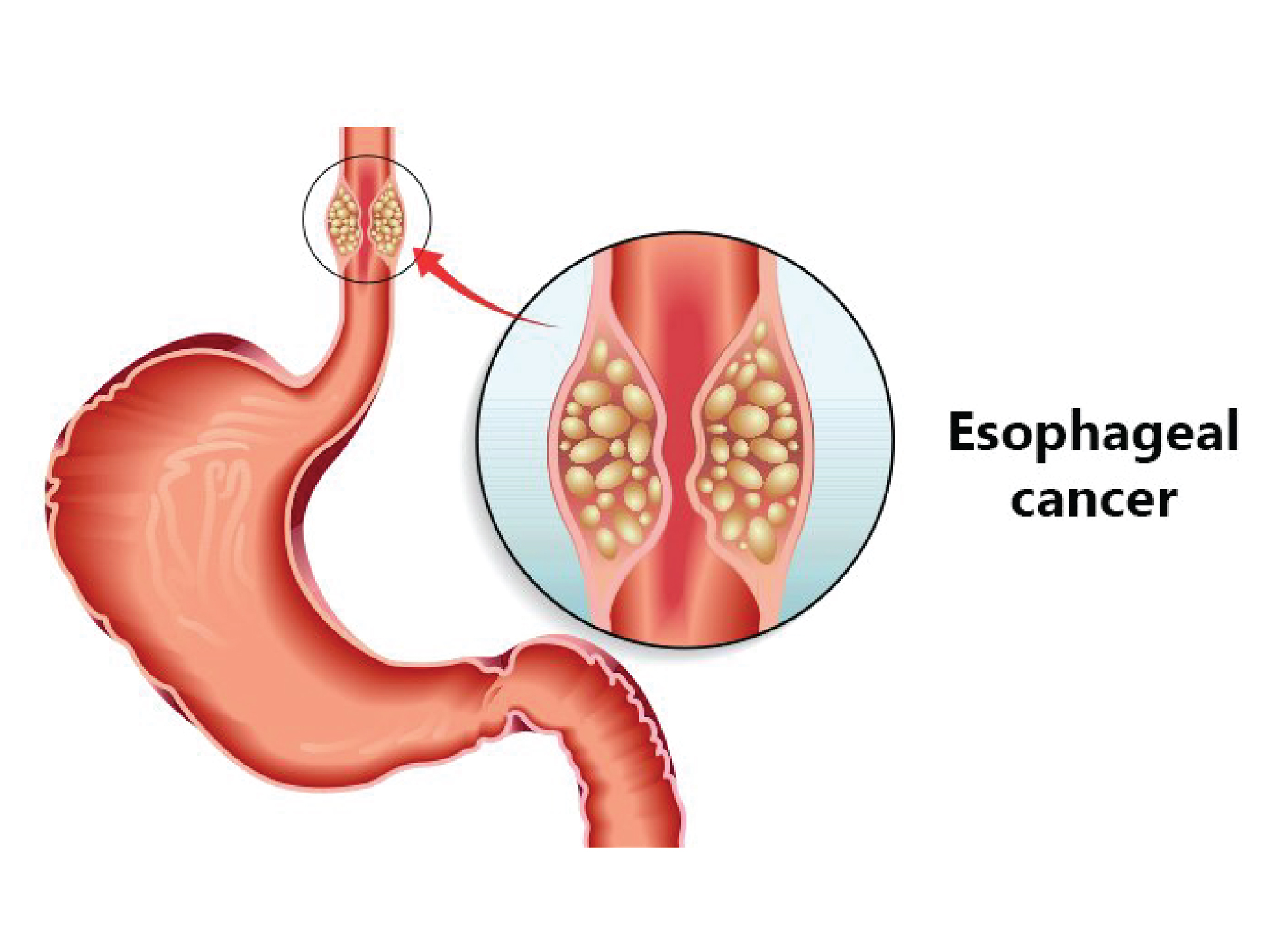
Types
There are two major types of esophageal cancer.
Risk factors
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called as risk factor.Risk factor of esophageal cancer include:
We don't yet know what exactly causes most esophageal cancers.


Symptoms
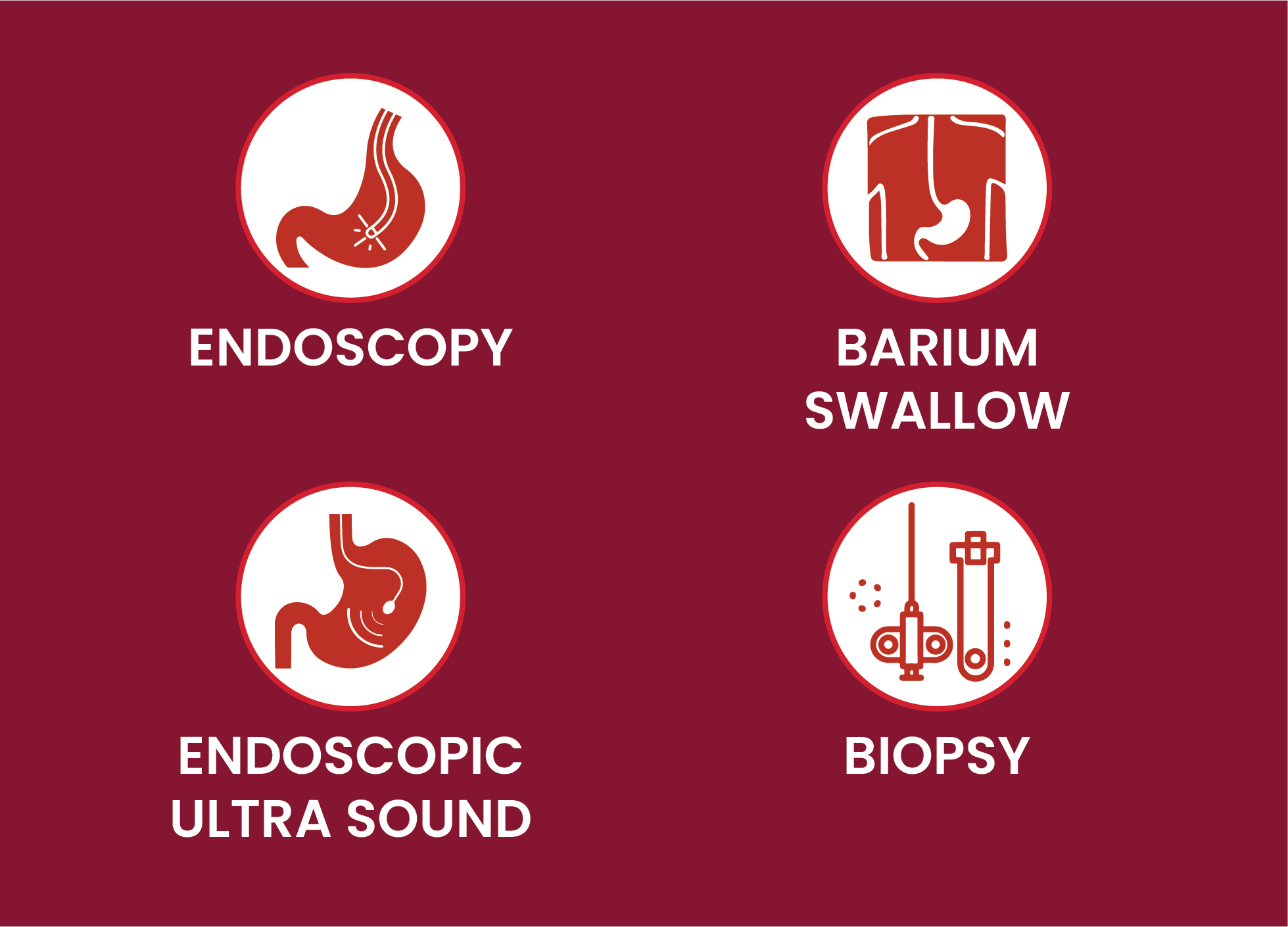
Diagnosis
To diagnose esophageal cancer, your health care professional will analyse your symptoms, medical history, and examine you. In addition, they may order some blood tests and X-rays.
Tests for esophageal cancer may include
Other tests, including computed tomography (CT) scans, positron emission tomography (PET) scan, thoracoscopy, and laparoscopy, may be carried out to determine if the cancer has spread, or metastasized, outside of the esophagus. This process is called "staging". The doctor needs this data in order to plan your treatment.
Treatment
As with numerous cancers, chances of survival increases if it is detected early. Unfortunately, by the time esophageal cancer is diagnosed for numerous people, it has spread throughout the esophagus and beyond.
Treatment depends on numerous factors, including the stage of the cancer and the overall health of the patient.
Endoscopic mucosal resection may be done to treat pre-cancers or veritably small early cancers by removing the inner lining of the esophagus. Radiofrequency ablation treatment using a device that targets cancer cells with radiofrequency energy is sometimes used for early cancers.
